Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition causing joint pain, inflammation, and stiffness, affecting daily activities.
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting millions worldwide. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, RA is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, primarily affecting the joints. Understanding RA's symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
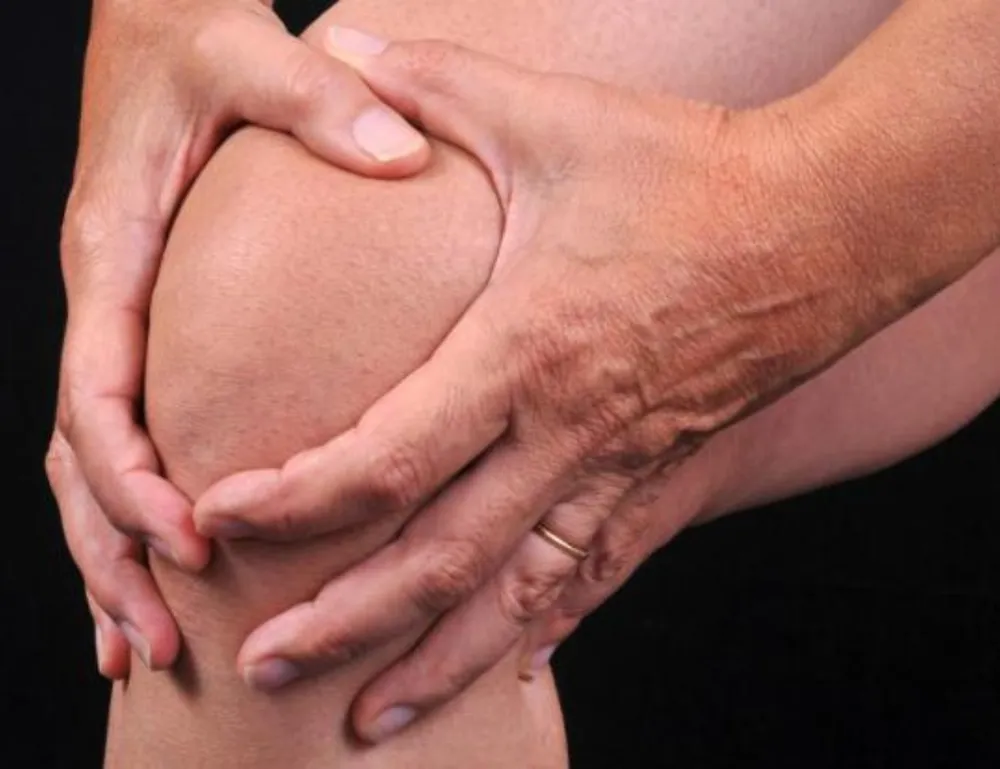
Joint Pain and Swelling
RA typically affects smaller joints first, such as those in the hands and feet. Over time, it can spread to larger joints like the knees, shoulders, and hips.

Morning Stiffness
Individuals with RA often experience stiffness in the affected joints, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity. This stiffness can last for hours.

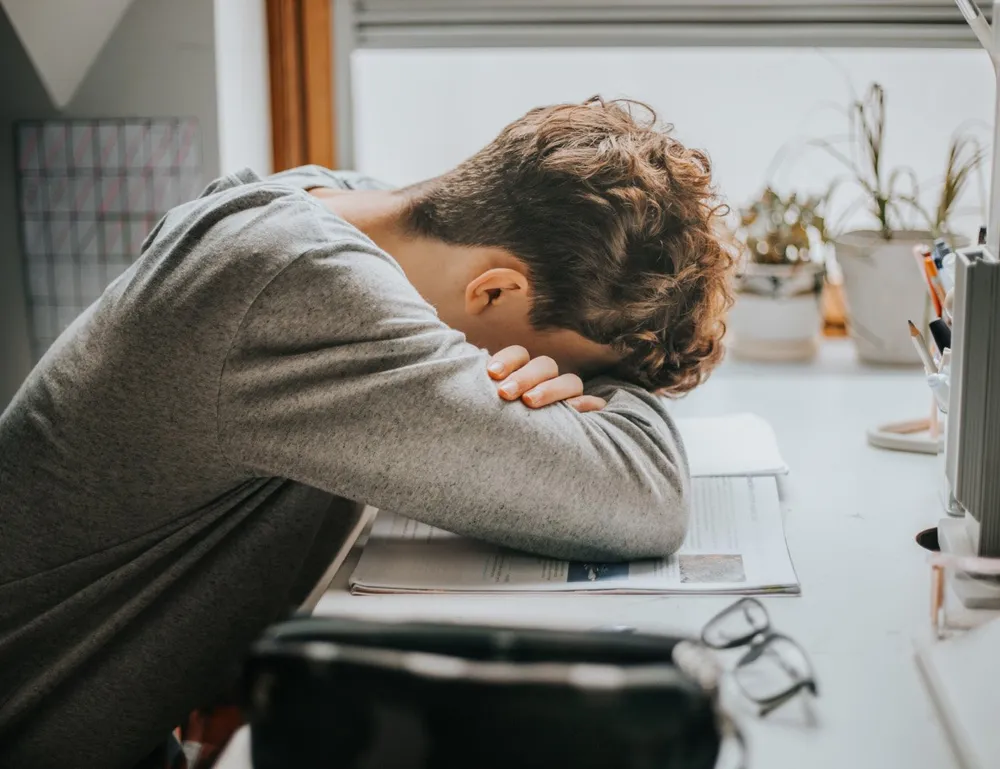
Fatigue
Chronic fatigue is a common symptom, often accompanied by a general feeling of malaise and tiredness.
Fever and Weight Loss
Low-grade fever and unintended weight loss can occur due to the body’s ongoing inflammatory response.

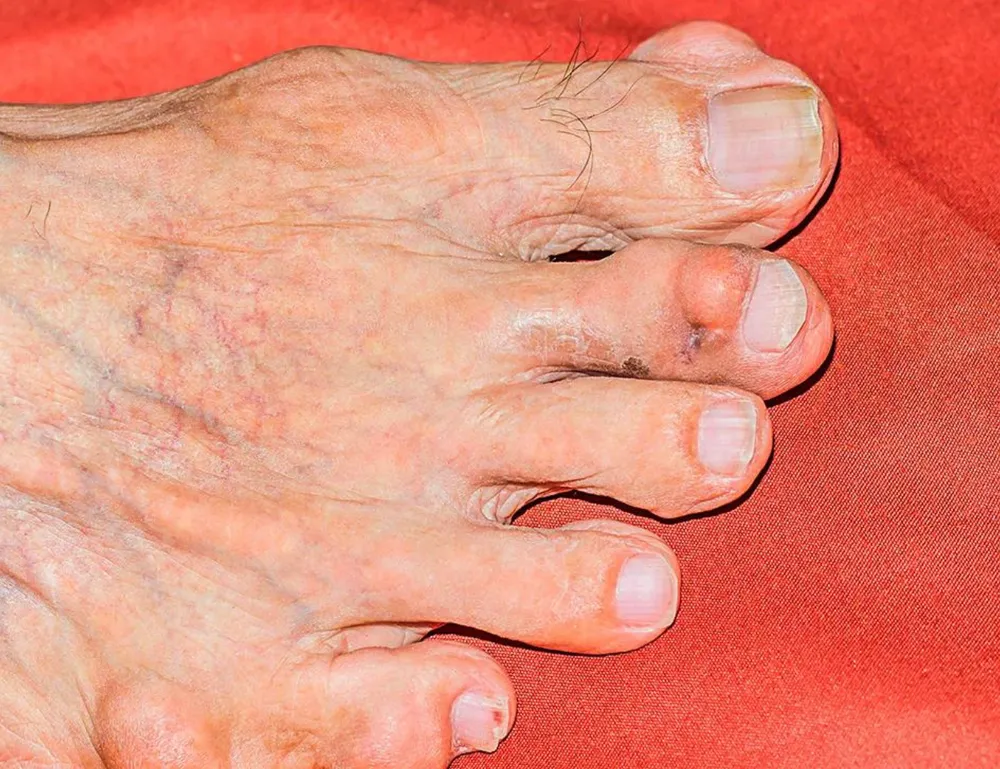
Nodules
Rheumatoid nodules, firm lumps under the skin, can develop near affected joints.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing support. Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis is essential for effective management and to prevent joint damage. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging studies.
Clinical Evaluation
A rheumatologist will review the patient’s medical history and perform a physical examination of the joints. They will check for signs like pain, stiffness, and swelling. The doctor may also ask detailed questions about the patient’s symptoms. This thorough assessment helps in diagnosing and managing Rheumatoid Arthritis.

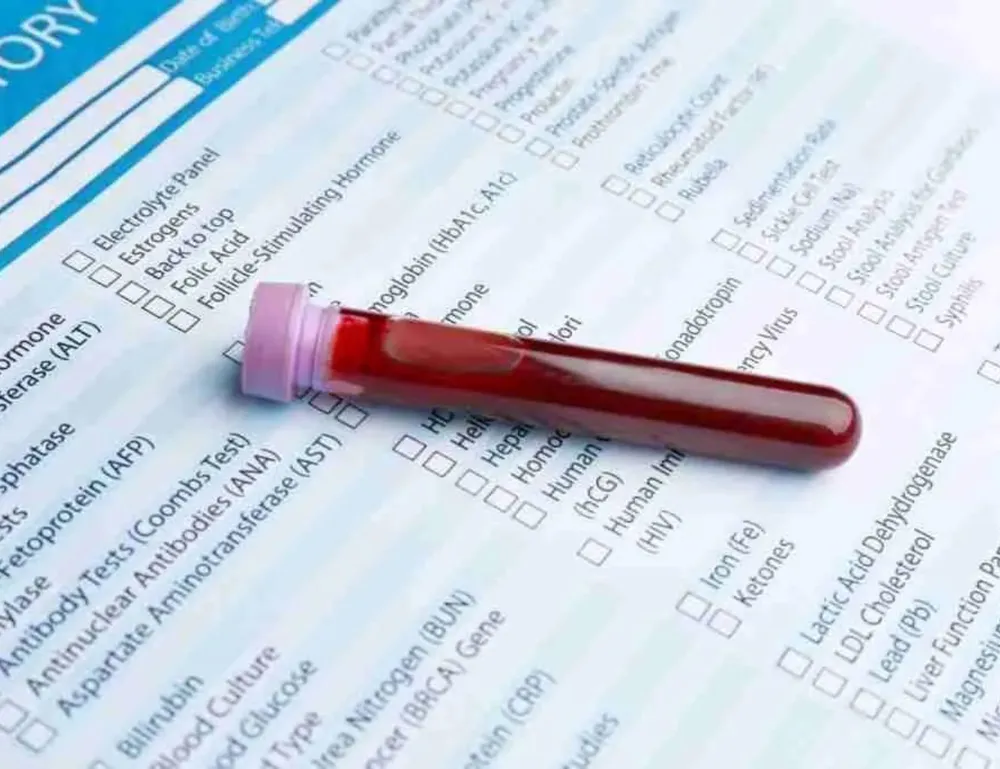
Blood Tests
Several blood tests help diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Factor (RF) antibodies are common in RA but can appear in other conditions. The Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) test is more specific to RA, aiding in diagnosis. Elevated ESR and CRP levels indicate inflammation, a key feature of RA.

Imaging Studies
X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRI scans are valuable tools for detecting joint damage and inflammation. They reveal bone erosion, cartilage loss, and swelling in the joints. These imaging studies provide a clearer understanding of how the disease is progressing. This helps doctors tailor treatment strategies more effectively.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
While there is no cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis, several treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow disease progression.
- Medications- Various medications are available to treat Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)- These drugs help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids- Prednisone and other corticosteroids can quickly reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)-DMARDs, such as methotrexate and sulfasalazine, help slow disease progression and prevent joint damage.
- Biologic Agents- Biologics, like tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and interleukin inhibitors, target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy- Physical therapy can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance overall mobility. A physical therapist can develop a customized exercise program to strengthen muscles around the joints and improve flexibility.
- Lifestyle Modifications- Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact managing Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Regular Exercise- Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, walking, and yoga, can help maintain joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Healthy Diet- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flax seed, have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Weight Management- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the joints and can alleviate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, which can exacerbate Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms.
- Surgery- In severe cases where joint damage is extensive, surgical options such as joint replacement or tendon repair may be necessary to restore function and reduce pain.

Tittle

Tittle

Tittle
Tittle
Support and Resources
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis can be challenging, but numerous resources and support networks are available to help patients cope with the physical and emotional aspects of the disease. Support groups, online communities, and patient education programs can provide valuable information and a sense of community. Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to manage effectively. By understanding the symptoms, pursuing an early diagnosis, and exploring various treatment options, individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis can lead fulfilling lives and minimize the impact of the disease on their daily activities. Regular communication with healthcare providers and staying informed about the latest advancements in Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment are essential steps in managing this chronic condition.